Appsmith AI
This page provides information on creating queries with Appsmith AI datasource, which allows you to configure applications with advanced AI features such as chat assistants, text generation, image classification, and sentiment analysis without the need for any API keys or datasource authentication.
Appsmith is committed to providing safe and responsible access to AI capabilities. Your prompts, outputs, embeddings, and data are not shared with other users and are never utilized to fine-tune models.
Connect Appsmith AI
Connection parameters
The following section is a reference guide that provides a complete description of all the parameters to connect to the datasource.
Files
You have the option to enhance text generation by uploading specific files for context. The maximum allowable file size is 20 MB; compress your file if the size exceeds 20 MB.
Submission of files is not mandatory, and you can use Appsmith AI without uploading any files.
For example, if you are working on a loan approval application and want to upload an SOP for insights into user preferences and financial details, the system uses the provided information to generate tailored recommendations and guidance.
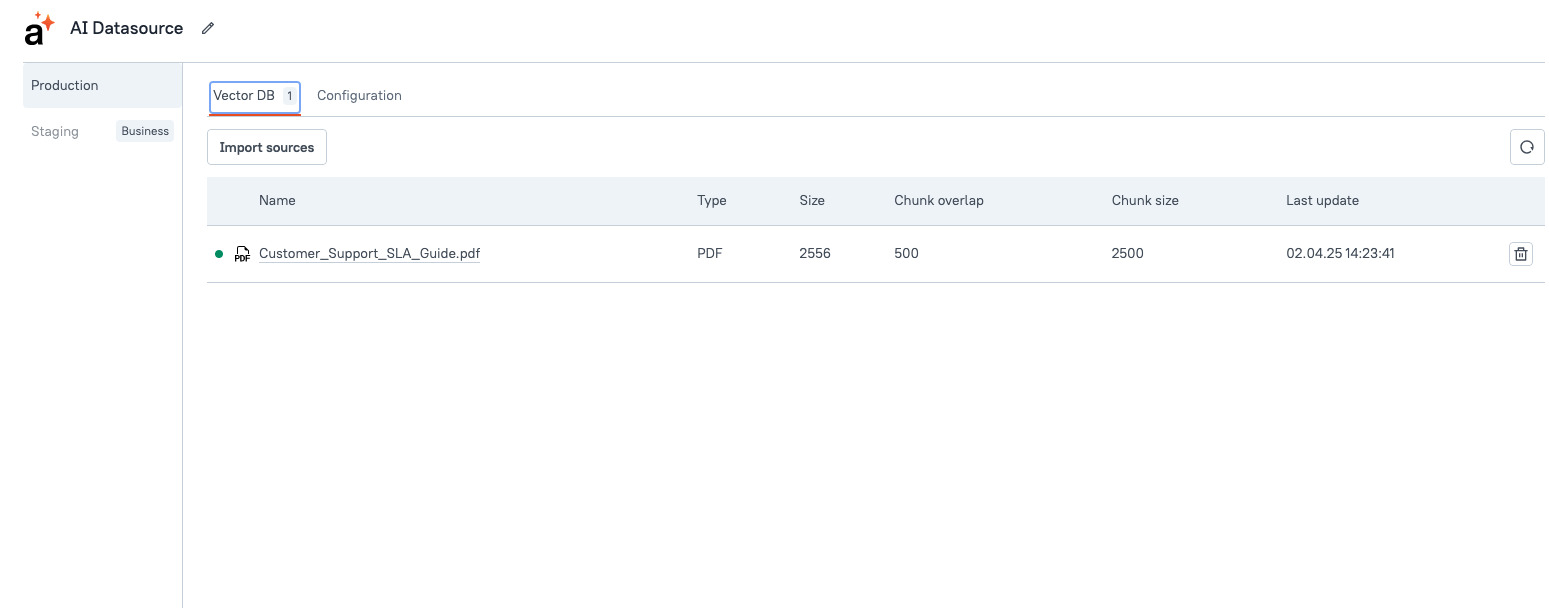
VectorDB
Allows you to connect to various datasources or upload files to provide additional context and enhance AI capabilities. Connected data or uploaded files can be referenced as citations in the AI Chat Widget, ensuring responses are backed by relevant information. You can resync, remove, or update uploaded files to ensure the AI Chat Assistant.
Available Options:
-
Google Drive: Connect to your Google account to upload files. You need to grant access to your Google Drive, including permissions to view and manage files, as well as view file metadata. You can connect multiple Google accounts and upload or delete files as needed.
-
Upload Files: Upload files directly from your local machine. You can upload multiple files of various types, including
.pdf,.docx,.txt, and others, with a maximum file size of 20 MB per file. -
Notion: Connect to your Notion account to sync and upload multiple Notion pages. The AI can reference your Notion content in responses, such as pulling information from your databases, pages, and blocks, to generate personalized replies.
-
Salesforce: Connect using your Salesforce URL, which can be found in your Salesforce account settings. You can connect multiple Salesforce accounts. This integration allows the AI to access your Salesforce data, such as retrieving leads, accounts, opportunities, and case details, to generate responses based on your CRM data.
-
Zendesk: Connect using your Zendesk domain to fetch ticket and customer information. You can connect multiple Zendesk accounts. This integration allows the AI to reference your Zendesk data in its responses, such as retrieving ticket details, fetching customer profiles, and analyzing support trends.
-
Web Scraper: This tool allows you to extract information from websites. This integration enables the AI to scrape data from specified web pages or sitemaps, pulling in details such as product listings, articles, or other structured content for use in generating responses or reports. When you click on Add URL, you can select between
WebsiteorSitemap.
- Website: Add multiple URLs and configure the following parameters to control the scraping process:
-
Recursion Depth: Specifies the number of link levels the scraper traverses from the initial URL. For instance, a recursion depth of 2 means the scraper will process the initial page (depth 0), pages linked directly from it (depth 1), and pages linked from those (depth 2).
-
Max Pages to Scrape: Defines the upper limit of pages to be processed. For example, setting this to 100 restricts the scraper to process only the first 100 pages encountered during the scraping process. These pages are typically processed in the order they are discovered (i.e., depth-first or breadth-first traversal), depending on the scraping logic, and not randomly.
- Sitemap Scraping: Provide a sitemap URL to direct the scraper in systematically identifying and extracting relevant pages. Sitemaps are structured XML files that list a website's important pages, facilitating efficient and comprehensive data extraction by outlining the site's structure.
Query Appsmith AI
The following section is a reference guide that provides a description of the available commands with their parameters to create Appsmith AI queries.
AI Chat Assistant
The AI Chat Assistant command allows you to interact with AI models using the AI Chat Widget. Users can input queries and receive AI-generated responses directly within the chat interface, without the need to bind or pass additional data.
System Instructions
The System Instructions property enables you to define specific behaviors and guidelines for the AI assistant, ensuring its responses align with your requirements.
You can also pass parameters between queries using this.params.name, allowing for a connected and dynamic experience.
Example: You want the AI assistant to help users fetch support ticket details. The user enters a prompt in the chat widget, such as “Can you check the status of ticket 498?”
You can extract the ticket ID from this prompt and pass it to the query as a parameter. In your query configuration, use {{this.params.id}} wherever the ticket ID is required.
For example, if you are querying a backend API or database:
SELECT * FROM tickets WHERE id = {{this.params.id}};
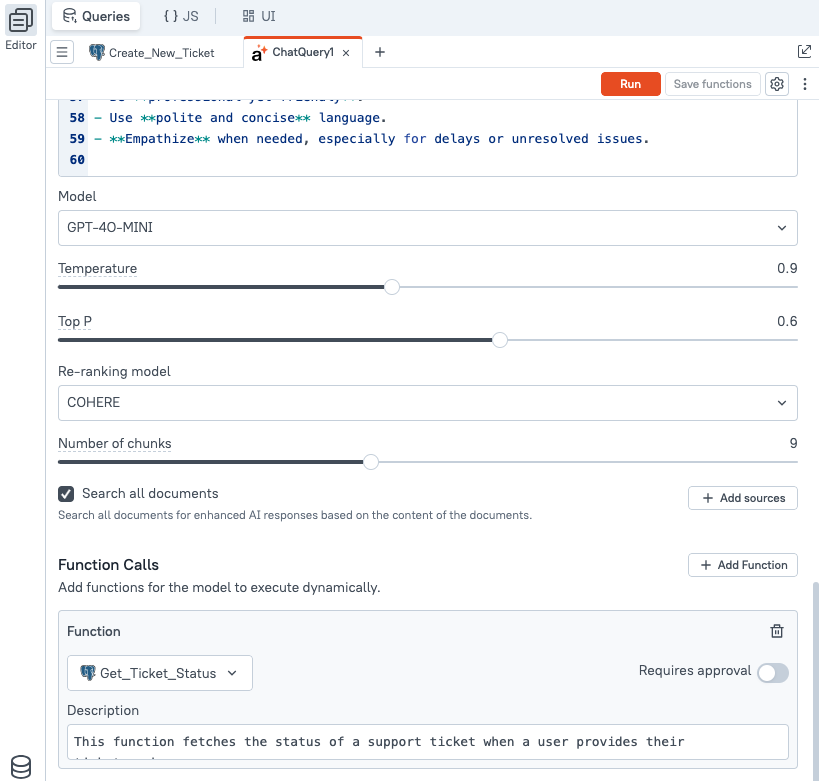
Model
The Model dropdown allows you to select the AI model to use for processing the chat prompt. Different models offer varying levels of performance, speed, and capability depending on the complexity of your use case.
Choosing the right model depends on the required response quality and system performance. If your application requires basic text generation or short responses, a lower-tier model may be sufficient. For more advanced use cases like summarization, multi-turn conversations, or data-driven assistance, higher-tier models are recommended.
Temperature
The Temperature parameter controls the randomness or creativity of the AI's responses. It accepts a numeric value ranging from 0 to 2.
-
A lower value (e.g., 0) results in more focused, predictable, and deterministic outputs. This is ideal for factual, structured, or repetitive tasks where consistency is important.
-
A higher value (e.g., 1.5 – 2) produces more creative, diverse, and open-ended responses, which may be useful for brainstorming, storytelling, or idea generation.
Top p
The Top P parameter (also known as nucleus sampling) controls the diversity of the AI’s responses by limiting the selection of next-word candidates to a subset of the most probable options.
It accepts a numeric value between 0 and 1:
-
A lower value (e.g., 0.1) restricts the output to only the top most likely tokens, making responses more focused and deterministic.
-
A higher value (e.g., 0.9 – 1) allows a wider range of possible outputs, increasing creativity and variability in the responses.
Top P is often used in conjunction with Temperature. While both influence randomness, Top P provides a probabilistic cutoff, whereas Temperature adjusts the sharpness of probability distribution. In most cases, adjusting one of the two is sufficient.
Re-ranking model
The Re-ranking Model setting determines how retrieved documents or contextual chunks are evaluated and ordered before being passed to the AI model. This is especially useful when working with file uploads or knowledge base applications where relevance ranking impacts the quality of responses.
Available options:
-
Cohere: Uses Cohere’s re-ranking model to score and reorder the most relevant document chunks based on semantic similarity to the user's input. This enhances response accuracy when multiple documents are involved.
-
Jina: Utilizes Jina AI’s re-ranking capabilities, which apply deep learning techniques to prioritize the most relevant content. Ideal for use cases requiring strong contextual alignment, such as AI support bots or content summarization.
-
None: Disables re-ranking. Documents are processed in their original order of retrieval. This may be faster but can reduce the relevance of the AI-generated response if many sources are involved.
Number of chunks
The Number of Chunks setting determines how many document or file chunks are retrieved and passed to the AI model as context during prompt execution. This is applicable when files are uploaded to enhance the assistant’s understanding of domain-specific information.
-
A lower value (e.g., 1–5) limits context to only the most relevant chunks, improving performance and reducing token usage.
-
A higher value (e.g., 15–20) includes more supporting content, which may improve accuracy for complex queries but could increase response time or cost.
Knowledge Source
You can add sources from the Appsmith AI Knowledge Base, which provides contextual information to enhance the accuracy and relevance of AI responses. These sources serve as reference material for the AI assistant when generating responses to user queries.
Appsmith AI allows you to connect various types of knowledge sources, including:
-
File Uploads: Add PDFs, Word documents, text files, and more.
-
Web Links: Provide URLs to publicly available content for AI to reference.
-
Connected SaaS Tools: Integrate with external tools such as Google Drive, Notion, Confluence, Jira, and others. This allows the assistant to access real-time or stored content from your organization’s systems.
You can select one or more knowledge sources based on your use case.
Example:
-
Select a Google Drive folder for a document-based assistant.
-
Add Jira as a source if the AI needs access to support tickets or engineering tasks.
-
Upload an internal training manual to help the AI guide new employees.
Function calls
The Function Calls feature allows you to extend the AI assistant’s capabilities by connecting it to custom backend logic. This enables dynamic, actionable experiences where the assistant can trigger application logic in response to user intent.
You can associate one or more Appsmith functions—such as queries, APIs, or JavaScript objects—with the AI assistant. When a user initiates a request like “Check ticket status” or “Update user profile,” the assistant can intelligently call the appropriate function and return the result directly in the chat interface.
This functionality empowers developers to build AI agents that go beyond simple Q&A by actively interacting with business data and services. Whether you are creating a customer support assistant, an internal operations bot, or a data retrieval tool, function calls allow the assistant to bridge user input with actionable outcomes—offering a intelligent application experience.
Example: Zendesk Ticket Assistant
Consider an AI assistant designed to help users with Zendesk ticket inquiries. You can configure the assistant to run two backend queries to fetch and display ticket details based on user input.
- Prompt example:
Can you show me the details of ticket ID 498?
- Function calls setup:
Query 1: getTicketDetails
SELECT * FROM zendesk_tickets WHERE ticket_id = {{ this.params.id }}
Query 2: getTicketComments
SELECT * FROM zendesk_comments WHERE ticket_id = {{ this.params.id }}
Execution flow:
-
The assistant extracts 498 from the prompt and assigns it to this.params.id.
-
Both queries are triggered using this dynamic parameter.
-
The results—ticket metadata and user comments—are returned in the assistant’s response.